
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Optimal Coefficient of Variance Threshold to Minimize Hypoglycemia Risk in Individuals with Well-Controlled Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jee Hee Yoo, Seung Hee Yang, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Received March 14, 2023 Accepted August 12, 2023 Published online March 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0083 [Epub ahead of print]

- 545 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the optimal coefficient of variance (%CV) for preventing hypoglycemia based on real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rt-CGM) data in people with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) already achieving their mean glucose (MG) target.
Methods
Data from 172 subjects who underwent rt-CGM for at least 90 days and for whom 439 90-day glycemic profiles were available were analyzed. Receiver operator characteristic analysis was conducted to determine the cut-off value of %CV to achieve time below range (%TBR)<54 mg/dL <1 and =0.
Results
Overall mean glycosylated hemoglobin was 6.8% and median %TBR<54 mg/dL was 0.2%. MG was significantly higher and %CV significantly lower in profiles achieving %TBR<54 mg/dL <1 compared to %TBR<54 mg/dL ≥1 (all P<0.001). The cut-off value of %CV for achieving %TBR<54 mg/dL <1 was 37.5%, 37.3%, and 31.0%, in the whole population, MG >135 mg/dL, and ≤135 mg/dL, respectively. The cut-off value for %TBR<54 mg/dL=0% was 29.2% in MG ≤135 mg/dL. In profiles with MG ≤135 mg/dL, 94.2% of profiles with a %CV <31 achieved the target of %TBR<54 mg/dL <1, and 97.3% with a %CV <29.2 achieved the target of %TBR<54 mg/ dL=0%. When MG was >135 mg/dL, 99.4% of profiles with a %CV <37.3 achieved %TBR<54 mg/dL <1.
Conclusion
In well-controlled T1DM with MG ≤135 mg/dL, we suggest a %CV <31% to achieve the %TBR<54 mg/dL <1 target. Furthermore, we suggest a %CV <29.2% to achieve the target of %TBR<54 mg/dL =0 for people at high risk of hypoglycemia.
Review
- Technology/Device
- Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
- Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):27-41. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0271

- 6,381 View
- 387 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology has evolved over the past decade with the integration of various devices including insulin pumps, connected insulin pens (CIPs), automated insulin delivery (AID) systems, and virtual platforms. CGM has shown consistent benefits in glycemic outcomes in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) treated with insulin. Moreover, the combined effect of CGM and education have been shown to improve glycemic outcomes more than CGM alone. Now a CIP is the expected future technology that does not need to be worn all day like insulin pumps and helps to calculate insulin doses with a built-in bolus calculator. Although only a few clinical trials have assessed the effectiveness of CIPs, they consistently show benefits in glycemic outcomes by reducing missed doses of insulin and improving problematic adherence. AID systems and virtual platforms made it possible to achieve target glycosylated hemoglobin in diabetes while minimizing hypoglycemia, which has always been challenging in T1DM. Now fully automatic AID systems and tools for diabetes decisions based on artificial intelligence are in development. These advances in technology could reduce the burden associated with insulin treatment for diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Accuracy and Safety of the 15-Day CareSens Air Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Won Sang Yoo, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024; 26(4): 222. CrossRef - Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sarah Andrade, Boyang Chen, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent advances in the precision control strategy of artificial pancreas
Wuyi Ming, Xudong Guo, Guojun Zhang, Yinxia Liu, Yongxin Wang, Hongmei Zhang, Haofang Liang, Yuan Yang
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital Health in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
Dorothy Avoke, Abdallah Elshafeey, Robert Weinstein, Chang H. Kim, Seth S. Martin
Endocrine Research.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring with structured education in adults with type 2 diabetes managed by multiple daily insulin injections: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kang Hee Sim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Jun Sung Moon, Soo Lim, Eun Seok Kang, Cheol-Young Park, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic Outcomes During Early Use of the MiniMed™ 780G Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop System with Guardian™ 4 Sensor
Toni L. Cordero, Zheng Dai, Arcelia Arrieta, Fang Niu, Melissa Vella, John Shin, Andrew S. Rhinehart, Jennifer McVean, Scott W. Lee, Robert H. Slover, Gregory P. Forlenza, Dorothy I. Shulman, Rodica Pop-Busui, James R. Thrasher, Mark S. Kipnes, Mark P. Ch
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(9): 652. CrossRef - Navigating the Seas of Glycemic Control: The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 345. CrossRef - APSec1.0: Innovative Security Protocol Design with Formal Security Analysis for the Artificial Pancreas System
Jiyoon Kim, Jongmin Oh, Daehyeon Son, Hoseok Kwon, Philip Virgil Astillo, Ilsun You
Sensors.2023; 23(12): 5501. CrossRef - Advances and Development of Electronic Neural Interfaces
Xue Jiaxiang, Liu Zhixin
Journal of Computing and Natural Science.2023; : 147. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) and Metabolic Control in a Cohort of Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Coeliac Disease
Flavia Amaro, Maria Alessandra Saltarelli, Marina Primavera, Marina Cerruto, Stefano Tumini
Endocrines.2023; 4(3): 595. CrossRef - Comparison of Glycemia Risk Index with Time in Range for Assessing Glycemic Quality
Ji Yoon Kim, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(12): 883. CrossRef - The Benefits Of Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Pregnancy
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 472. CrossRef - The Growing Challenge of Diabetes Management in an Aging Society
Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 630. CrossRef - Recent advances in artificial intelligence-assisted endocrinology and diabetes
Ioannis T. Oikonomakos, Ranjit M. Anjana, Viswanathan Mohan, Charlotte Steenblock, Stefan R. Bornstein
Exploration of Endocrine and Metabolic Disease.2023; 1(1): 16. CrossRef - An Observational Pilot Study of a Tailored Environmental Monitoring and Alert System for Improved Management of Chronic Respiratory Diseases
Mohammed Alotaibi, Fady Alnajjar, Badr A Alsayed, Tareq Alhmiedat, Ashraf M Marei, Anas Bushnag, Luqman Ali
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2023; Volume 16: 3799. CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef
- Accuracy and Safety of the 15-Day CareSens Air Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
Corrigendum
- Time in Range from Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Novel Metric for Glycemic Control
- Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):795-795. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0256
- Corrects: Diabetes Metab J 2020;44(6):828
- 2,946 View
- 92 Download
Original Article
- Complications
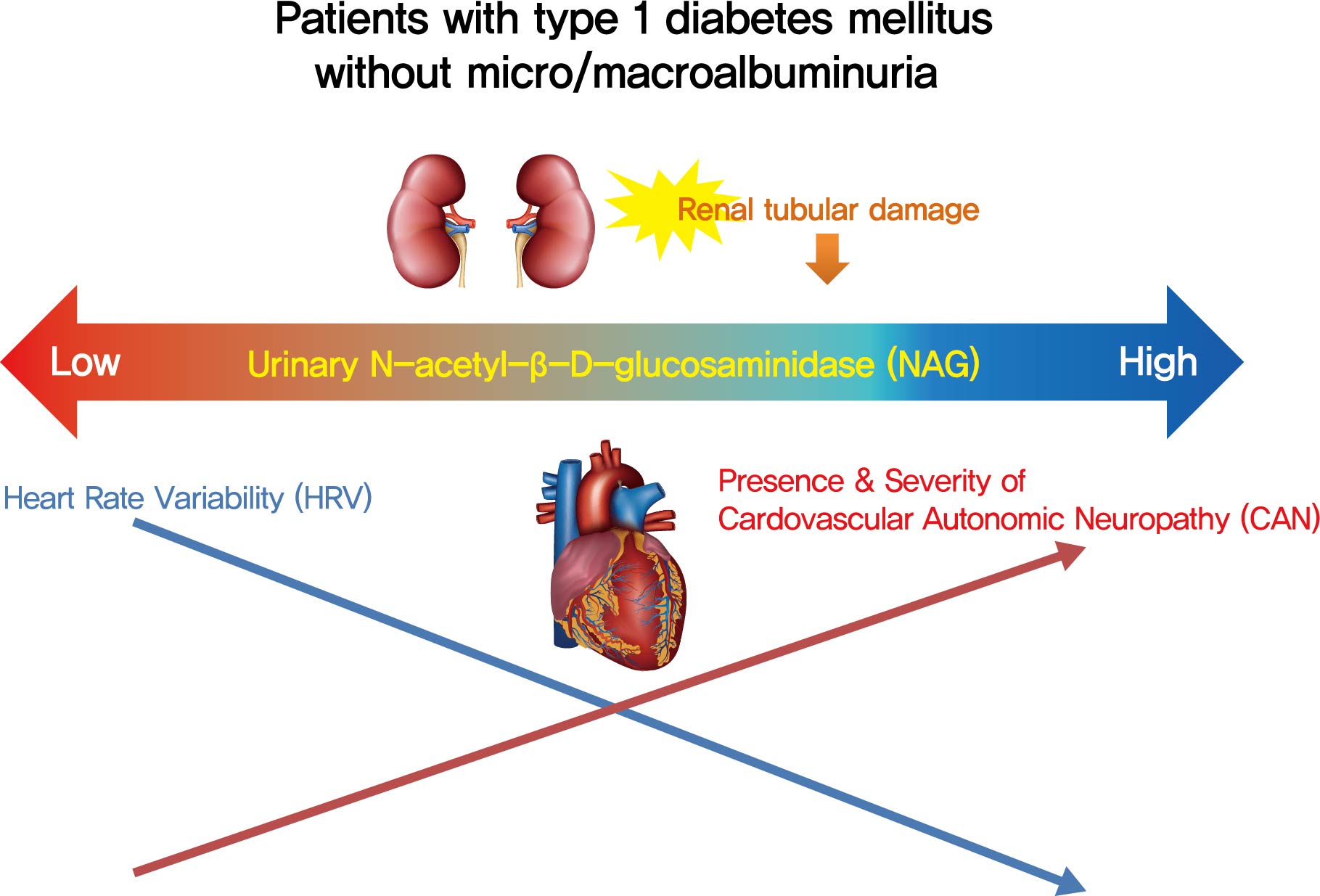
- Association of Urinary N-Acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase with Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus without Nephropathy
- Min Sun Choi, Ji Eun Jun, Sung Woon Park, Jee Hee Yoo, Jiyeon Ahn, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):349-357. Published online February 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0211
- 5,659 View
- 121 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (CAN) is a common microvascular complication of diabetes and related to albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy (DN). Urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (uNAG) is a renal tubular injury marker which has been reported as an early marker of DN even in patients with normoalbuminuria. This study evaluated whether uNAG is associated with the presence and severity of CAN in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) without nephropathy.
Methods
This cross-sectional study comprised 247 subjects with T1DM without chronic kidney disease and albuminuria who had results for both uNAG and autonomic function tests within 3 months. The presence of CAN was assessed by age-dependent reference values for four autonomic function tests. Total CAN score was assessed as the sum of the partial points of five cardiovascular reflex tests and was used to estimatethe severity of CAN. The correlations between uNAG and heart rate variability (HRV) parameters were analyzed.
Results
The association between log-uNAG and presence of CAN was significant in a multivariate logistic regression model (adjusted odds ratio, 2.39; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.08 to 5.28; P=0.031). Total CAN score was positively associated with loguNAG (β=0.261, P=0.026) in the multivariate linear regression model. Log-uNAG was inversely correlated with frequency-domain and time-domain indices of HRV.
Conclusion
This study verified the association of uNAG with presence and severity of CAN and changes in HRV in T1DM patients without nephropathy. The potential role of uNAG should be further assessed for high-risk patients for CAN in T1DM patients without nephropathy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Determination of Diabetes-associated Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Risk Factors among Insulin and Non-insulin Dependent Diabetics
Ibrahim Abdulsada, Zain Alabdeen Obaid, Farah Almerza, Mays Alwaeli, Anmar Al-Elayawi, Taha Al-Dayyeni, Harir Al-Tuhafy
The Journal of Medical Research.2023; 9(6): 141. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef
- Determination of Diabetes-associated Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Risk Factors among Insulin and Non-insulin Dependent Diabetics
Review
- Type 1 Diabetes
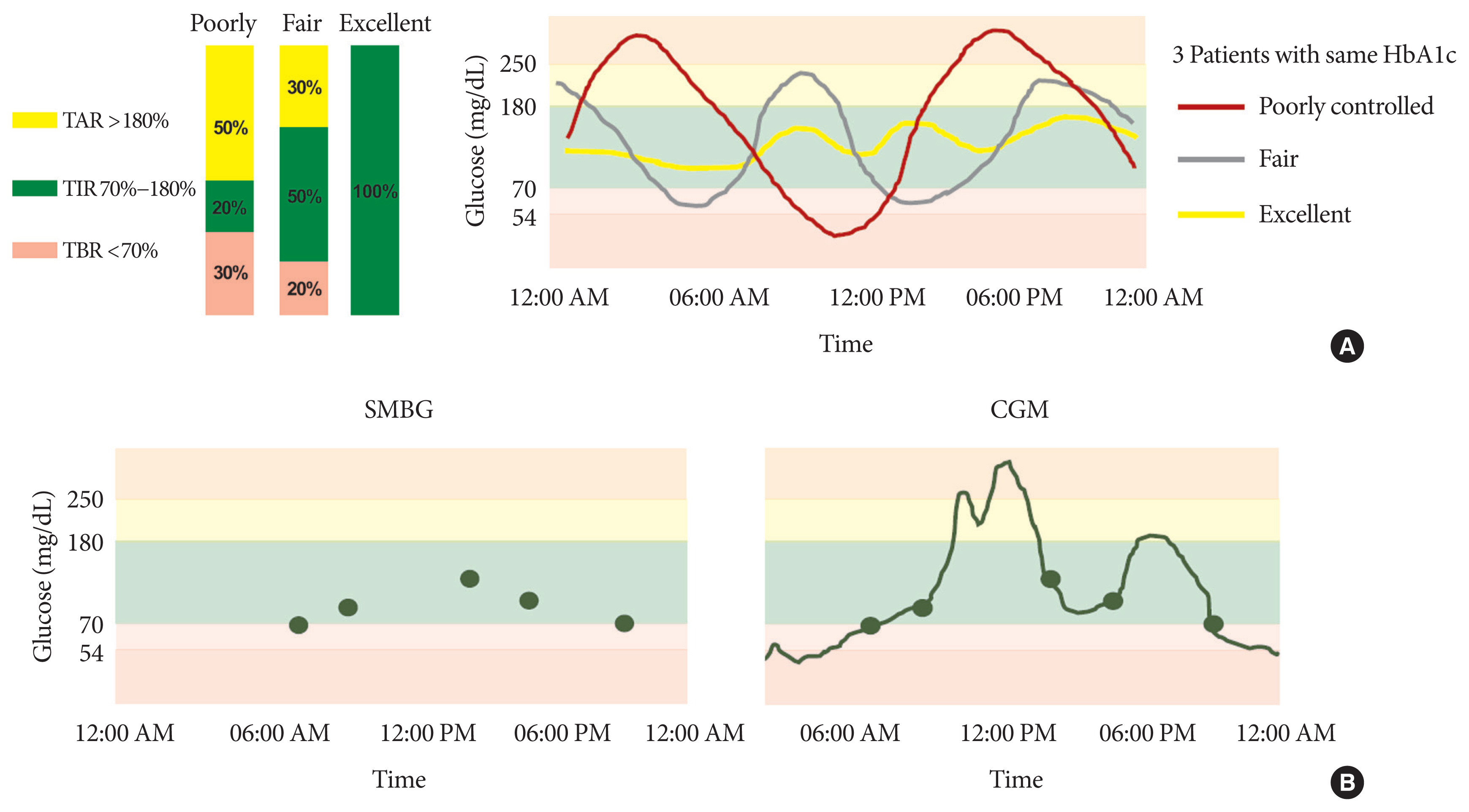
- Time in Range from Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Novel Metric for Glycemic Control
- Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):828-839. Published online December 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0257
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2021;45(5):795
- 9,879 View
- 469 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 36 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) has been the sole surrogate marker for assessing diabetic complications. However, consistently reported limitations of HbA1c are that it lacks detailed information on short-term glycemic control and can be easily interfered with by various clinical conditions such as anemia, pregnancy, or liver disease. Thus, HbA1c alone may not represent the real glycemic status of a patient. The advancement of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has enabled both patients and healthcare providers to monitor glucose trends for a whole single day, which is not possible with HbA1c. This has allowed for the development of core metrics such as time spent in time in range (TIR), hyperglycemia, or hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability. Among the 10 core metrics, TIR is reported to represent overall glycemic control better than HbA1c alone. Moreover, various evidence supports TIR as a predictive marker of diabetes complications as well as HbA1c, as the inverse relationship between HbA1c and TIR reveals. However, there are more complex relationships between HbA1c, TIR, and other CGM metrics. This article provides information about 10 core metrics with particular focus on TIR and the relationships between the CGM metrics for comprehensive understanding of glycemic status using CGM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Acute and Chronic Adverse Outcomes of Type 1 Diabetes
Rachel Longendyke, Jody B. Grundman, Shideh Majidi
Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America.2024; 53(1): 123. CrossRef - La plongée sous-marine en scaphandre autonome avec un diabète de type 1. Une belle histoire du dernier millénaire
Lise Dufaitre Patouraux, Agnès Sola-Gazagnes, Boris Lormeau, Corinne Lormeau
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2024; 18(1): 67. CrossRef - S100A9 exerts insulin-independent antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory effects
Gloria Ursino, Giulia Lucibello, Pryscila D. S. Teixeira, Anna Höfler, Christelle Veyrat-Durebex, Soline Odouard, Florian Visentin, Luca Galgano, Emmanuel Somm, Claudia R. Vianna, Ariane Widmer, François R. Jornayvaz, Andreas Boland, Giorgio Ramadori, Rob
Science Advances.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hybrid Closed-Loop Versus Manual Insulin Delivery in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: A Post Hoc Analysis Using the Glycemia Risk Index
Melissa H. Lee, Sara Vogrin, Timothy W. Jones, David N. O’Neal
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinically relevant stratification of patients with type 2 diabetes by using continuous glucose monitoring data
Xiaopeng Shao, Jingyi Lu, Rui Tao, Liang Wu, Yaxin Wang, Wei Lu, Hongru Li, Jian Zhou, Xia Yu
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a 2-Week Kinect-Based Mixed-Reality Exercise Program on Prediabetes: A Pilot Trial during COVID-19
So Young Ahn, Si Woo Lee, Hye Jung Shin, Won Jae Lee, Jun Hyeok Kim, Hyun-Jun Kim, Wook Song
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2024; 33(1): 54. CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring with structured education in adults with type 2 diabetes managed by multiple daily insulin injections: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kang Hee Sim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Jun Sung Moon, Soo Lim, Eun Seok Kang, Cheol-Young Park, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison between a tubeless, on-body automated insulin delivery system and a tubeless, on-body sensor-augmented pump in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Eun Seok Kang, Soo Heon Kwak, Yeoree Yang, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyun Bae, Jun Sung Moon, Chang Hee Jung, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh, Sun Joon Moon, Sun Ok Song, Suk Chon, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Anagliptin twice‐daily regimen improves glycaemic variability in subjects with type 2 diabetes: A double‐blind, randomized controlled trial
Yong‐ho Lee, Doo‐Man Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Kyung Mook Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Kang Seo Park, Hyun‐Shik Son, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Soon Hee Lee, Ki‐Ho Song, Su Kyoung Kwon, Hyeong Kyu Park, Kyu Chang Won, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(5): 1174. CrossRef - Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 27. CrossRef - Status of continuous glucose monitoring use and management in tertiary hospitals of China: a cross-sectional study
Liping Chen, Xiaoqin Liu, Qin Lin, Hongmei Dai, Yong Zhao, Zumin Shi, Liping Wu
BMJ Open.2023; 13(2): e066801. CrossRef - Real-world outcomes of continuous glucose monitoring in adults with diabetes mellitus attending an Irish tertiary hospital
Aoife Courtney, Diarmuid Smith, Hannah Forde
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2023; 192(6): 2763. CrossRef - Insight into continuous glucose monitoring: from medical basics to commercialized devices
Ayman Chmayssem, Małgorzata Nadolska, Emily Tubbs, Kamila Sadowska, Pankaj Vadgma, Isao Shitanda, Seiya Tsujimura, Youssef Lattach, Martin Peacock, Sophie Tingry, Stéphane Marinesco, Pascal Mailley, Sandrine Lablanche, Pierre Yves Benhamou, Abdelkader Zeb
Microchimica Acta.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of polyethylene glycol loxenatide versus insulin glargine on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, open-label, parallel-group trial
Shuo Zhang, Chuanyan Zhang, Jingxian Chen, Feiying Deng, Zezhen Wu, Dan Zhu, Fengwu Chen, Yale Duan, Yue Zhao, Kaijian Hou
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control and its derived metrics in type 1 diabetes: a longitudinal study
So Hyun Cho, Seohyun Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Glycemia Risk Index and Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes
Jee Hee Yoo, Ji Yoon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(10): 726. CrossRef - Acute Glycemic Variability and Early Outcomes After Cardiac Surgery:
A Meta-Analysis
Shuo Chang, Mian Xu, Yu Wang, Yanbo Zhang
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2023; 55(11): 771. CrossRef - Comparison of Glycemia Risk Index with Time in Range for Assessing Glycemic Quality
Ji Yoon Kim, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(12): 883. CrossRef - Correlação entre tempo no alvo e hemoglobina glicada de pessoas com diabetes mellitus: revisão sistemática
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlación entre tiempo en rango y hemoglobina glicosilada en personas con diabetes mellitus: revisión sistemática
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation between time on target and glycated hemoglobin in people with diabetes mellitus: systematic review
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef - Novel Glycemic Index Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Predict Poor Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Il Rae Park, Yin Young Lee, Eun Young Choi, Jun Sung Moon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypoglycemic agents and glycemic variability in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
SuA Oh, Sujata Purja, Hocheol Shin, Minji Kim, Eunyoung Kim
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2022; 19(3): 147916412211068. CrossRef - Advanced Glycation End Products and Their Effect on Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jeongmin Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3086. CrossRef - Influence of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on glycemic variability in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Shangyu Chai, Ruya Zhang, Ye Zhang, Richard David Carr, Yiman Zheng, Swapnil Rajpathak, Miao Yu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Glucose Profiles Assessed by Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring System during the Perioperative Period of Metabolic Surgery
Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang, Young Suk Park, Tae Jung Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 713. CrossRef - Deterioration in glycemic control on schooldays among children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A continuous glucose monitoring-based study
Yu Ding, Wenhao Zhang, Xiumei Wu, Tian Wei, Xulin Wang, Xueying Zheng, Sihui Luo
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of repeated bolus and continuous glucose infusion on a panel of circulating biomarkers in healthy volunteers
Roland Feldbauer, Matthias Wolfgang Heinzl, Carmen Klammer, Michael Resl, Johannes Pohlhammer, Klemens Rosenberger, Verena Almesberger, Florian Obendorf, Lukas Schinagl, Thomas Wagner, Margot Egger, Benjamin Dieplinger, Martin Clodi, Stephen L. Atkin
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(12): e0279308. CrossRef - Relationship between glycemic intraday variations evaluated in continuous glucose monitoring and HbA1c variability in type 2 diabetes: pilot study
Akemi Tokutsu, Yosuke Okada, Keiichi Torimoto, Yoshiya Tanaka
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Time-in-range for monitoring glucose control: Is it time for a change?
Virginia Bellido, Pedro José Pinés-Corrales, Rocío Villar-Taibo, Francisco Javier Ampudia-Blasco
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 177: 108917. CrossRef - Glucose Management Indicator for People with Type 1 Asian Diabetes Is Different from That of the Published Equation: Differences by Glycated Hemoglobin Distribution
Jee Hee Yoo, Seung Hee Yang, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life, Family Conflicts and Fear of Injecting: Perception Differences between Preadolescents and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes and Their Mothers
Marta Tremolada, Maria Cusinato, Sabrina Bonichini, Arianna Fabris, Claudia Gabrielli, Carlo Moretti
Behavioral Sciences.2021; 11(7): 98. CrossRef - Daytime Glycemic Variability and Frailty in Older Patients with Diabetes: a Pilot Study Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Seung Min Chung, Yun Hee Lee, Chang Oh Kim, Ji Yeon Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Seung-Hyun Yoo, Jun Sung Moon, Kwang Joon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Benefits of a Switch from Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring (isCGM) to Real-Time (rt) CGM in Diabetes Type 1 Suboptimal Controlled Patients in Real-Life: A One-Year Prospective Study §
Yannis Préau, Sébastien Galie, Pauline Schaepelynck, Martine Armand, Denis Raccah
Sensors.2021; 21(18): 6131. CrossRef - Recent Advances of Integrative Bio-Omics Technologies to Improve Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Care
Nisha Karwal, Megan Rodrigues, David D. Williams, Ryan J. McDonough, Diana Ferro
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(24): 11602. CrossRef
- Acute and Chronic Adverse Outcomes of Type 1 Diabetes

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





